A Definition of AGI
Dan Hendrycks1, Dawn Song2,3, Christian Szegedy4, Honglak Lee5,6, Yarin Gal7
Erik Brynjolfsson8, Sharon Li9, Andy Zou1,10,11, Lionel Levine12, Bo Han13, Jie Fu14, Ziwei Liu15
Jinwoo Shin16, Kimin Lee16, Mantas Mazeika1, Long Phan1, George Ingebretsen1
Adam Khoja1, Cihang Xie17, Olawale Salaudeen18, Matthias Hein19, Kevin Zhao20
Alexander Pan2, David Duvenaud21,22, Bo Li3,23, Steve Omohundro24, Gabriel Alfour25
Max Tegmark18, Kevin McGrew26, Gary Marcus27, Jaan Tallinn28
Eric Schmidt18, Yoshua Bengio29,30
Dan Hendrycks1, Dawn Song2,3, Christian Szegedy4
Honglak Lee5,6, Yarin Gal7, Erik Brynjolfsson8
Sharon Li9, Andy Zou1,10,11, Lionel Levine12
Bo Han13, Jie Fu14, Ziwei Liu15
Jinwoo Shin16, Kimin Lee16, Mantas Mazeika1
Long Phan1, George Ingebretsen1, Adam Khoja1
Cihang Xie17, Olawale Salaudeen18, Matthias Hein19
Kevin Zhao20, Alexander Pan2, David Duvenaud21,22
Bo Li3,23, Steve Omohundro24, Gabriel Alfour25
Max Tegmark18, Kevin McGrew26, Gary Marcus27
Jaan Tallinn28, Eric Schmidt18, Yoshua Bengio29,30
1Center for AI Safety
2University of California, Berkeley
3Virtue AI
4Morph Labs
5University of Michigan
6LG AI Research
7University of Oxford
8Stanford University
9University of Wisconsin–Madison
10Gray Swan AI
11Carnegie Mellon University
12Cornell University
13Hong Kong Baptist University
14HKUST
15Nanyang Technological University
16KAIST
17University of California, Santa Cruz
18Massachusetts Institute of Technology
19University of Tübingen
20University of Washington
21University of Toronto
22Vector Institute
23University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign
24Beneficial AI Research
25Conjecture
26Institute for Applied Psychometrics
27New York University
28CSER
29Université de Montréal
30LawZero
Introduction
The lack of a concrete definition for Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) obscures the gap between today’s specialized AI and human-level cognition. This paper introduces a quantifiable framework to address this, defining AGI as matching the cognitive versatility and proficiency of a well-educated adult. To operationalize this, we ground our methodology in Cattell-Horn-Carroll theory, the most empirically validated model of human cognition.
The framework dissects general intelligence into ten core cognitive domains—including reasoning, memory, and perception—and adapts established human psychometric batteries to evaluate AI systems. Application of this framework reveals a highly “jagged” cognitive profile in contemporary models. While proficient in knowledge-intensive domains, current AI systems have critical deficits in foundational cognitive machinery, particularly long-term memory storage.
The resulting AGI scores (e.g., GPT-4 at 27%, GPT-5 at 57%) concretely quantify both rapid progress and the substantial gap remaining before AGI.
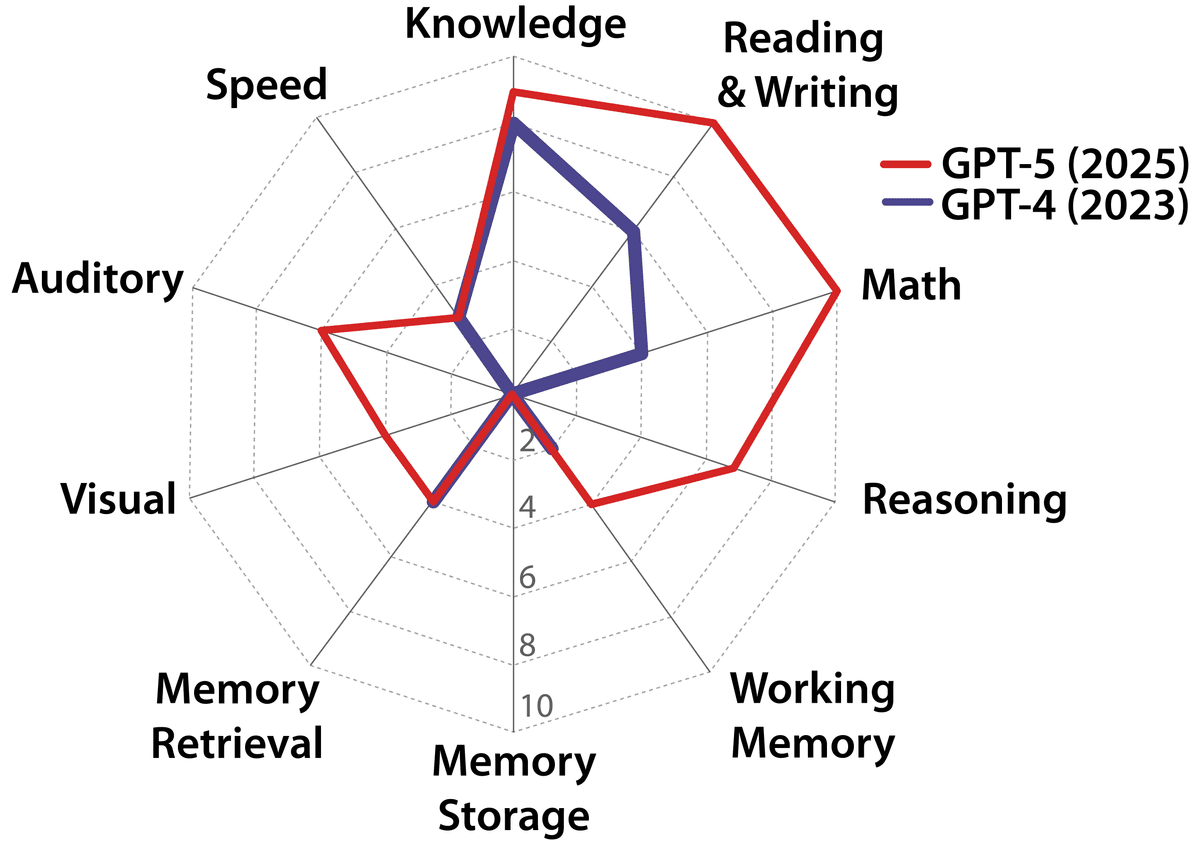
The capabilities of GPT-4 and GPT-5.
Definition
"AGI is an AI that can match or exceed the cognitive versatility and proficiency of a well-educated adult."
The framework comprises ten core cognitive components, derived from CHC broad abilities and weighted equally (10%) to prioritize breadth and cover major areas of cognition:
Acquired Knowledge
Perception
Central Executive
Output
Citation
@misc{hendrycks2025definitionagi,
title={A Definition of AGI},
author={Dan Hendrycks and Dawn Song and Christian Szegedy and Honglak Lee and Yarin Gal and Erik Brynjolfsson and Sharon Li and Andy Zou and Lionel Levine and Bo Han and Jie Fu and Ziwei Liu and Jinwoo Shin and Kimin Lee and Mantas Mazeika and Long Phan and George Ingebretsen and Adam Khoja and Cihang Xie and Olawale Salaudeen and Matthias Hein and Kevin Zhao and Alexander Pan and David Duvenaud and Bo Li and Steve Omohundro and Gabriel Alfour and Max Tegmark and Kevin McGrew and Gary Marcus and Jaan Tallinn and Eric Schmidt and Yoshua Bengio},
year={2025},
eprint={2510.18212},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.AI},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.18212},
}